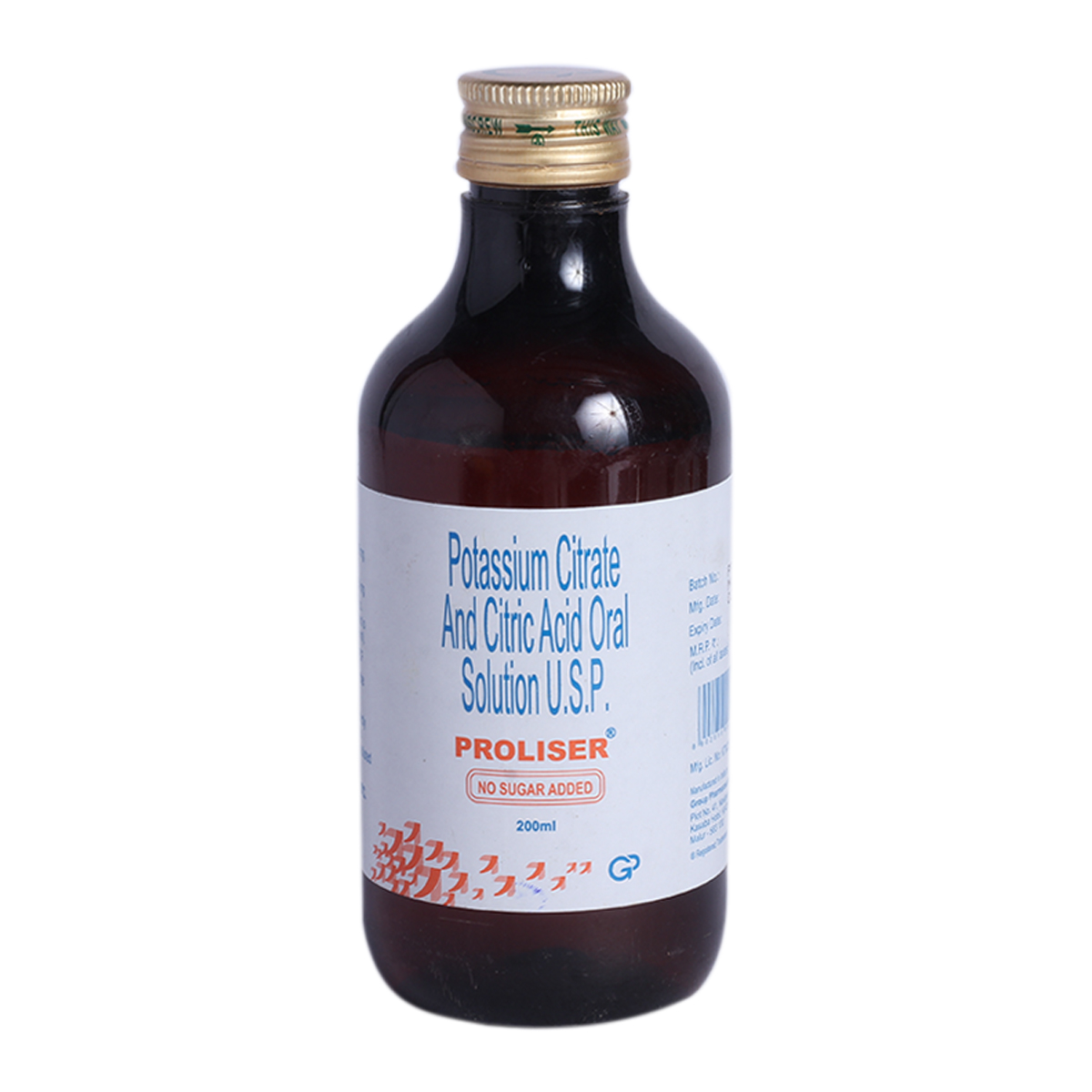
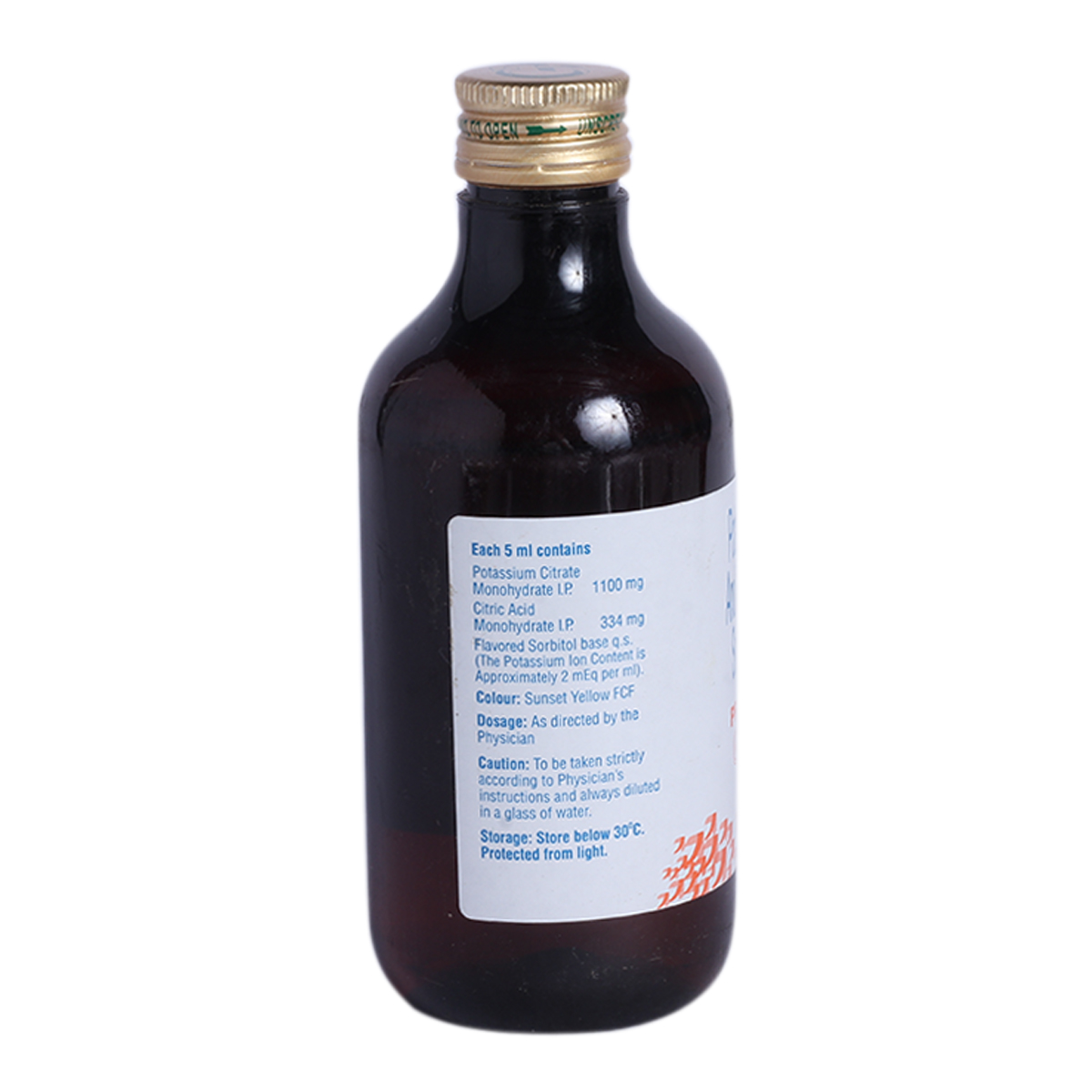
Proliser Syrup
MRP ₹161
(Inclusive of all Taxes)
₹24.1 Cashback (15%)


Available Offers
Therapeutic Class
Author Details
We provide you with authentic, trustworthy and relevant information
Drug-Drug Interactions Checker List
- ALUMINUM CARBONATE
- ALUMINUM HYDROXIDE
- ASPIRIN
- LITHIUM
- METHENAMINE
- QUINIDINE
- TRIAMTERENE
- SPIRONOLACTONE
- AMILORIDE
- DIPHENHYDRAMINE
- BROMPHENIRAMINE
- ENALAPRIL
- CAPTOPRIL
- FOSINOPRIL
- AMITRIPTYLINE
- AMOXAPINE
- DOXEPIN
- IMIPRAMINE
- SOLIFENACIN
- DARIFENACIN
Drug Warnings
Proliser Syrup should be used with caution in patients with fluid loss (dehydration), heat cramps, high potassium levels, a certain problem that causes periods of muscle weakness (adynamia episodica hereditaria), kidney disease, heart disease, unable to pass urine, or untreated Addison's disease, toxaemia of pregnancy (high blood pressure during pregnancy), oedema (swelling), and chronic diarrhoea. Do not take antacids without consulting your doctor while using Proliser Syrup , as it may lead to electrolyte imbalances. Proliser Syrup should not be used in pregnancy or breastfeeding unless the doctor has told you to do so. Do not take food containing potassium supplements or other products that contain potassium, as they may worsen your condition. Stop using Proliser Syrup and consult a doctor immediately if you notice muscle twitching, swelling, weakness, mood changes, weight gain, increased heart rate, black or tarry stools, severe diarrhoea, or convulsions (fits) while using Proliser Syrup .
Side Effects of Proliser Syrup
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diahrrea
- Stomach upset
- Black, tarry, or bloody stools
Directions for Use
Medicinal Benefits Mweb
Key Benefits
Proliser Syrup is a combination of two medicines: Citric acid and Potassium citrate, primarily used to prevent gout and kidney stones and treat metabolic acidosis in patients with kidney diseases. Citric acid prevents the formation of deposits by binding with the salts and also breaks down the small deposits that are beginning to form. Potassium citrate is alkaline in nature and works by neutralizing the acids in the blood and urine. Proliser Syrup effectively reduces the crystallization of stone-forming salts such as calcium oxalate (in kidney stones) and uric acid (in gout).
Uses of Proliser Syrup
About Proliser Syrup
Proliser Syrup belongs to the class of medications called ‘alkalinizing agents’ used to prevent gout and kidney stones and treat metabolic acidosis in patients with kidney diseases. Gout is a type of arthritis in which uric acid crystals are deposited in the joints leading to severe pain, redness, and swelling. A kidney stone is a condition in which hard deposits are accumulated in the kidney forming stones. Metabolic acidosis is a condition in which excess acid is accumulated in the body due to kidney failure.
Proliser Syrup combines two medicines: Citric acid and Potassium citrate. Citric acid prevents the formation of deposits by binding with the salts and also breaks down the small deposits that are beginning to form. Potassium citrate is alkaline in nature and works by neutralizing the acids in the blood and urine, thereby preventing the accumulation of salts in the body.
Proliser Syrup is available in the form of oral liquid. You should take this medicine as prescribed by your doctor. Proliser Syrup may cause side effects such as diarrhoea, stomach upset, nausea, and vomiting. These side effects are mild and temporary. However, inform your doctor if any of these side effects persist or get worsen.
To treat your condition, continue taking Proliser Syrup for as long as your doctor has prescribed it. Do not take Proliser Syrup if you are allergic to Citric acid, potassium citrate, or other ingredients. Inform your doctor if you are pregnant or breastfeeding before taking the Proliser Syrup . It should not be used in patients with severe kidney failure, severe heart damage, severe dehydration, heat cramps, Addison’s disease (an adrenal gland disorder), or hyperkalemia (high blood potassium levels). Proliser Syrup should not be given to children unless prescribed by a doctor. Avoid alcohol consumption while taking Proliser Syrup as it might increase certain side-effects. Keep your doctor informed about all the medicines you are taking and your health condition to rule out any unpleasant side effects.
Online payment accepted
know your delivery time
Provide Delivery Location
Author Details
We provide you with authentic, trustworthy and relevant information
Therapeutic Class
All Substitutes & Brand Comparisons
RX
Out of StockK-Cit Oral Solution 300 ml
Dr Reddy's Laboratories Ltd
₹142
(₹0.43/ 1ml)
40% CHEAPERRX
Uricure Syrup 200 ml
₹140.5
(₹0.63/ 1ml)
12% CHEAPERRX
Alkamax Syrup 200 ml
Overseas Health Care Pvt Ltd
₹161.5
(₹0.73/ 1ml)
1% COSTLIER

Have a query?
Verified Buyers Reviews
Buy best Genito Urinary products by
Cipla Ltd
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
Intas Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Ipca Laboratories Ltd
Leeford Healthcare Ltd
Dr Reddy's Laboratories Ltd
Lupin Ltd
Alkem Laboratories Ltd
Msn Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Zydus Healthcare Ltd
Demorbus India Pvt Ltd
Mankind Pharma Pvt Ltd
Overseas Health Care Pvt Ltd
RPG Life Sciences Ltd
La Renon Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Alembic Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Corona Remedies Pvt Ltd
Macleods Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Aristo Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Fourrts India Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Tas Med India Pvt Ltd
Micro Labs Ltd
Samarth Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Zydus Cadila
Emcure Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Hetero Drugs Ltd
Ignyx Pharmaceuticals
Renspur Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Steris Healthcare
Alniche Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Septalyst Lifesciences Pvt Ltd
Ajanta Pharma Ltd
Elder Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Merynova Life Sciences India Pvt Ltd
Tppl Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Walter Bushnell
Aar Ess Remedies Pvt Ltd
Knoll Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Lividus Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Meditrex Pharma
Medrhans Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Neuten HealthCare
Redmed Medical Services
Talohsty Medmark Pvt Ltd
Zycris Healthcare
East West Pharma India Pvt Ltd
Globus Remedies Ltd
Golden Square Lab Pvt Ltd
Hetero Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Modi Mundipharma Pvt Ltd
Nephurocare Pharma Pvt Ltd
Pfizer Ltd
TTK Healthcare Ltd
Votary Laboratories (India) Ltd
Albus Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Delvin Formulations (P) Ltd
Indoco Remedies Ltd
Intra Life Pvt Ltd
Megma Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Morepen Laboratories Ltd
Qren Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Steadfast MediShield Pvt Ltd
Unipark Biotech Pvt Ltd
Akumentis Healthcare Ltd
Biokindle Lifesciences Pvt Ltd
Calren Care Lifesciences Pvt Ltd
Chemo Biological Ltd
Chemo Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Euniche Life Sciences
Himeros Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Hospimax Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Kiosence Health Care Pvt Ltd
Lia Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Panacea Biotec Ltd
Primus Remedies Pvt Ltd
Rencord Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Shilpa Medicare Ltd
Stadmed Pvt Ltd
Abbott India Ltd
Ameya Pharmaceuticals & Chemicals Pvt Ltd
Ardent Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Asterima Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Astrum Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Cadila Healthcare Ltd
De Renon
Fibovil Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Koye Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Linux Laboratories Pvt Ltd
MMC Healthcare Ltd
Neovae Biomedics Pvt Ltd
Olcare Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Oxygen Pharma Care Pvt Ltd
Prevego Healthcare & Research Pvt Ltd
Rene Lifescience
Sanzyme Pvt Ltd
Solis Ortus Remedies Pvt Ltd
Syndicate Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Tycoon Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Vasu Organics Pvt Ltd
Walron Health Care Pvt Ltd
Customers Also Bought
Frequently Bought Together
₹292.5
MRP ₹344
15% off
1
+₹388.3
MRP ₹410
5% off
1
+